Child labor’s public perception problem

Reid Maki is the director of child labor advocacy at the National Consumers League and he coordinates the Child Labor Coalition.
There are a lot of obstacles to ending child labor that the Child Labor Coalition (CLC) and its nearly 40 members confront on a daily basis. Poverty, governmental indifference, educational access, and a lack of awareness of the long-term impact of child labor on children are all big factors, but another is lack of knowledge of the scope or prevalence of the problem. The average American consumer doesn’t understand that child labor is a pervasive problem affecting an estimated 152 million children in the world—and that’s an estimate developed before the pandemic started. We think the number has grown significantly since COVID started throwing hundreds of millions of families into deeper poverty.
We became aware of the gap between the public’s perception of the problem and the reality of the situation seven years ago when the group Child Fund International commissioned a survey of over 1,000 consumers. Only one percent knew that roughly 150 million children were trapped in child labor globally. Even more disturbing: 73 percent of respondents—essentially three out of four—incorrectly guessed that the global total was less the one million. They were off by a factor of 150!
It’s hard to galvanize public and political opinion to confront a pressing social problem when few people realize the massive scope of the problem and instead misperceive it as a tiny, moribund problem. If we want corporations that benefit from child labor to take serious action, we need a better understanding of the problem’s prevalence. Governments are not likely to act or expend financial resources on programs to fix a problem perceived as affecting very few children.
We’ve been wondering if the Internet and Twitter have helped close the perception gap in the several years since Child Fund’s polling. Surveys are expensive and our budget didn’t allow us to conduct a phone-based survey like the 2013 poll. So, we decided to use a Survey Monkey internet poll to see where the public’s perception levels were at. We conducted the poll before COVID struck.
We gave respondents the opportunity to guess how many children were impacted by child labor and offered the following choices:
- 1 in 10
- 1 in 100
- 1 in 500
- 1 in 1,000
- 1 in 5,000
- 1 in 50,000
The most popular answer was the correct one: “1 in 10.” Thirty-five percent guessed correctly that 10 percent of the world’s children toil in child labor. However, that means that roughly two out of three respondents were off by a factor of 10 or more.
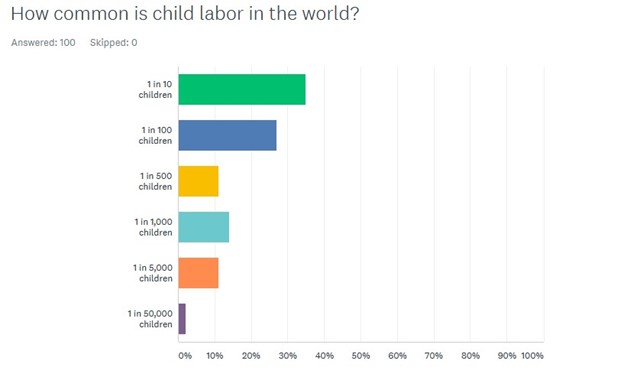
We think the answers in our informal internet poll may have skewed toward a better knowledge of the problem because we advertised the survey on our Twitter (@ChildLaborCLC), meaning it was being seen by people who presumably had better knowledge about child labor than the random public. With two-thirds of the public off by a factor of 100 or more, we know we still have a lot of work to do to close the perception gap.
In the last decade, the CLC has posted nearly 11,000 tweets to increase public understanding that child labor is a widespread and pernicious problem. We’re also active on Facebook (@ChildLaborCoalition) and our website (stopchildlabor.org) generates about 100,000 visits a year.
Those efforts don’t seem to be enough and we could use your help in the fight to end child labor. Please follow our posts and share them. Be a warrior in the fight to end child labor!
Remember that Child Fund International poll in 2013 we started with? The good news revealed in that survey was that more than half (55 percent) of the respondents said they would pay more for clothing made without child labor. They said they would pay 34 percent more on average for clothing untainted by child labor! According to cleanclothes.org, labor costs are typically less than 3 percent of clothing costs. Ending child labor would not raise prices significantly.
Garments are just one of 150 products identified by the U.S. Department of Labor “Sweat and Toil” app as being produced with child labor. If consumers are willing to pay more for child labor free clothing, they are likely to pay more for all products without child exploitation. That’s very encouraging.
The Child Labor Coalition is co-chaired by the National Consumers League and the American Federation of Teachers. Consumers who wish to donate to help reduce child labor can do so here.







 By NCL Director of Health Policy Jeanette Contreras
By NCL Director of Health Policy Jeanette Contreras

 Hispanic Heritage Month: Focus on the importance of participating in research through clinical trials
Hispanic Heritage Month: Focus on the importance of participating in research through clinical trials