NCL testified before FDA committee meeting on Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine
For immediate release: December 11, 2020
Media contact: National Consumers League – Carol McKay, carolm@nclnet.org, (412) 945-3242 or Taun Sterling, tauns@nclnet.org, (202) 207-2832
Washington, DC – The National Consumers League (NCL) testified before the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) this week regarding the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine.
“As the nation’s oldest consumer advocacy organization, NCL has been encouraged by the honesty, transparency, and access afforded to the public during this critical time.” NCL commended the Food and Drug Administration, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and other public health entities for their commitment to fostering public trust throughout the COVID-19 vaccine development and approval process and thanked the committee for the opportunity to speak.
In its testimony, NCL noted that there has never been a more critical time for consumers to have confidence in the FDA.
Emergency Use Authorization (EUA):
The FDA has undergone scrutiny from the scientific community for prematurely issuing EUAs for COVID-19 therapeutics. NCL is aware that developing a vaccine for COVID-19 is a time-sensitive priority and appreciates that the FDA recognizes that an EUA is not intended to replace long-term randomized clinical trials data associated with full FDA approval. We are encouraged by data reporting a consistent vaccine efficacy rate of 95 percent across age, gender, race, and ethnicity demographics and look forward to seeing more guidance around the vaccine, as the trial continues to collect safety and efficacy data.
Safety and Effectiveness:
NCL noted the public’s growing trust in the FDA’s rigorous vaccine approval process and called on the agency to perform ongoing post-market surveillance. Such surveillance performed in the United Kingdom found that the vaccine may be unsafe for individuals with severe allergies. Consumers will rely on ongoing guidance from public health agencies regarding any potential adverse events from the vaccine and expect that the FDA will be aware of these concerns.
Innovative Vaccine Delivery Systems:
Additionally, ensuring innovative vaccine delivery methods, such as including oral or nasal options, could address geographical access issues, diverse health needs, and increase uptake overall.
Diversity in Clinical Trials:
We applaud Pfizer’s efforts to ensure diversity in their COVID-19 vaccine clinical trials. NCL requests that the FDA continue to prioritize vaccine clinical trial data that reflects diversity, as people of color will need to have confidence in the vaccine’s efficacy. This will affect the overall uptake of the vaccine.
The development of a COVID-19 vaccine in such a short time frame is a huge scientific feat, made possible through robust collaboration between private and public entities. NCL will continue to support the FDA and CDC in efforts to release a COVID-19 vaccine safely and expeditiously.
###
About the National Consumers League (NCL)
The National Consumers League, founded in 1899, is America’s pioneer consumer organization. Our mission is to protect and promote social and economic justice for consumers and workers in the United States and abroad. For more information, visit www.nclnet.org.




 By NCL Director of Health Policy Jeanette Contreras
By NCL Director of Health Policy Jeanette Contreras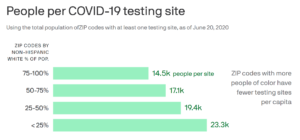


 Hispanic Heritage Month: Focus on the importance of participating in research through clinical trials
Hispanic Heritage Month: Focus on the importance of participating in research through clinical trials
 By NCL Executive Assistant Adrienne Archer
By NCL Executive Assistant Adrienne Archer The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has observed a sharp increase in those that, in addition to ethanol, also contain
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has observed a sharp increase in those that, in addition to ethanol, also contain 












